Shift Differential for an Hourly Work Period
A shift differential is used to apply a specific rate to a shift where a worker qualifies for that rate. The rate is a modifier where an hourly time card is specified for the engagement. For more information about hourly time cards, see Time Card Types.
The four types of differentials that you can define for a shift in a work period are as
follows:
- Time Span - This type corresponds to any time span less than or equal to 24 hours. Time span start/end times cannot overlap in a workday, for example, T1-6am to 1pm and T2-11am to 2pm cannot be used on the same entry on a timecard. The sum of the start/end times must be exactly 24 hours.
- Name - This can be any definition. This shift type should only be used if the associated timecard does not include a start/end time section.
- Specific Day - This type corresponds to a 24 hour time period (full day).
- Holiday - This type represents a 24 hour period that corresponds to a defined
client location holiday. The worker record must have the correct Holiday
Category. Holiday shift differentials are available for all hourly and daily
timecards.Note: Both holidays and specific days use the 'day' definition in the work period (when the day begins and when the day ends).
You can define additional differentials for a defined shift differential type. For example, when using the Name type, which allows a worker to select a shift at a certain position with a different bill rate, the application can determine the modified rate for hours entered for that selection. See the following screen shot.
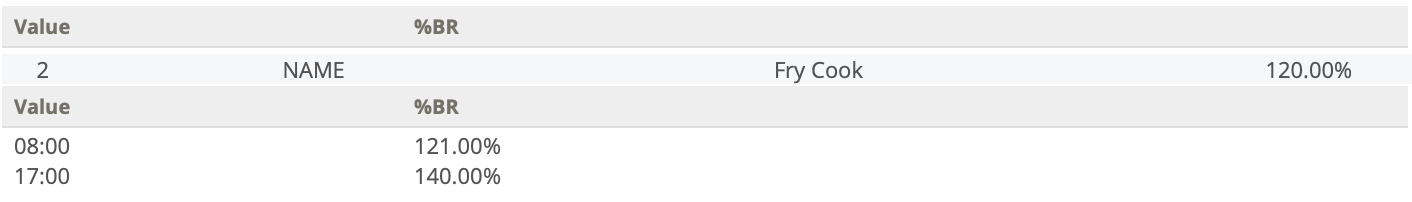
For hours entered between 8:00 am and 5:00 pm, the worker receives 121% of the bill rate.
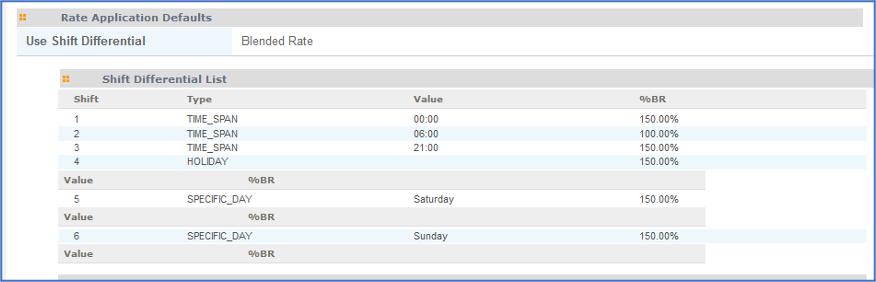
If you are adding multiple differential types for an engagement, it is recommended that
the shifts are added in the following order:
- Time Span
- Name
- Specific Day
- Holiday
For example:
Additionally, you can apply overtime and/or double time rules on top of the shift
differential. For more information about applying overtime rules, see Overtime Rules Application.
Note: Shift differentials cannot be
associated to payroll engagements.